How and why to use white label to validate your prototypes
White label design has emerged as a popular strategy for many design and development teams to build a product that multiple companies can purchase and redesign. It usually takes a lot of time and resources to design and develop tools, applications and webWhat is White Labeling
White labeling is the process of rebranding a single product or service for multiple companies to sell as their own. White labeling benefits the manufacturer and the reseller. The manufacturer can focus on production and not worry about marketing and selling, while the reseller can outsource production and focus on selling products through its sales and distribution networks.
White Label on CMS
It's a code-free app to help marketers, designers and development staff to optimize customer experiences quickly and easily. Anyone - regardless of skill - can point, click and customize the content. In the CMS, you can customize a user interface allowing professionals to perform combined, personalized profile management activities in one place and launch it as a network of websites.
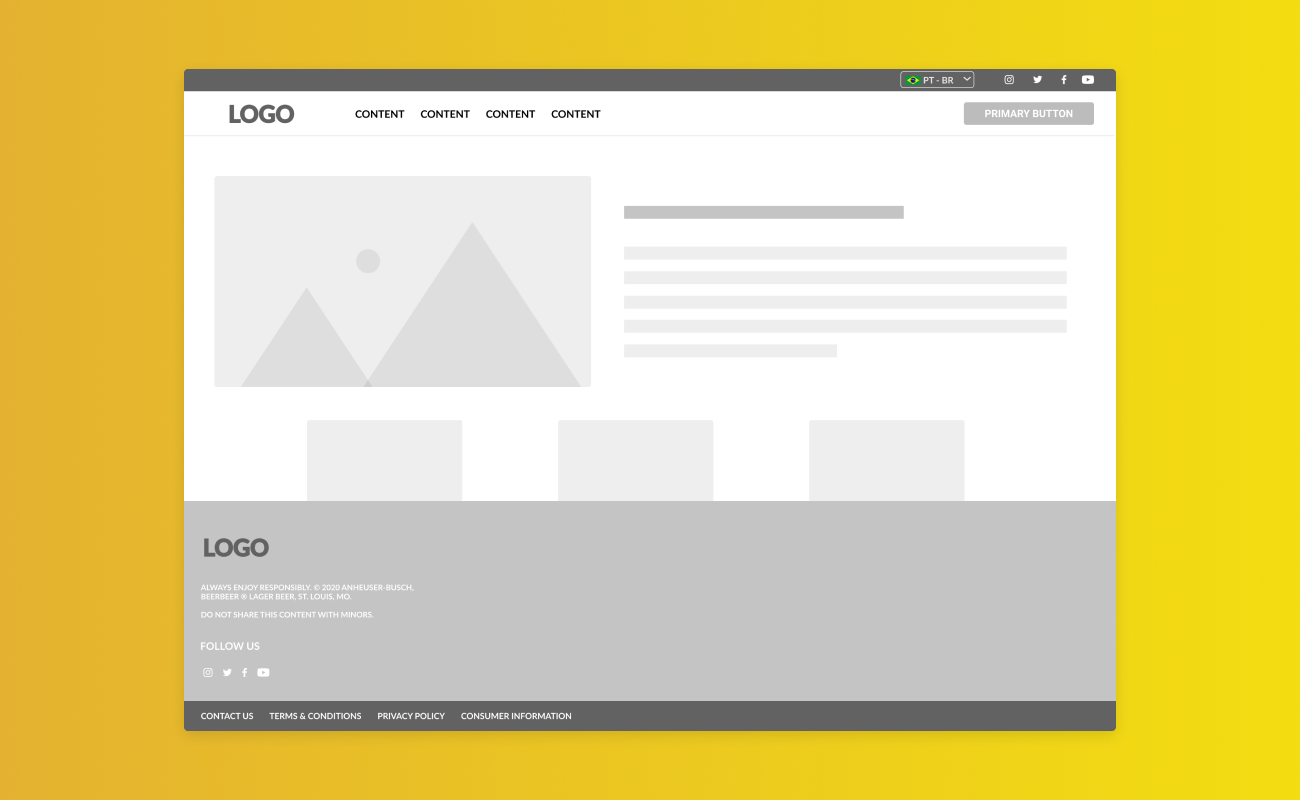
Impress your clients with a branded landing page. Add yours or your client’s logo, add a background image and even control the CSS if you wish. Personalising the back end of WordPress will give your client the feeling that this is their website, not a generic website.

White Label Design System
A successful white label product features a flexible, well-structured design system that can adapt to any brand’s style guide. The goal is to facilitate significant changes with the slightest design system edits.
For example, changing the color palette with a few HEX code modifications.
Following atomic design principles can facilitate the flexibility required for a white label design system, starting with the smallest elements, which designers can build components for multiple page layout possibilities.
Instead of limiting designs to specific pages, designers use components to build features and layouts—providing customers with flexibility and customization through simple drag-and-drop changes.
We can break a white label design system into three parts:
• Elements – colors, typefaces, icons, grids, spacing, brand assets
• Components – buttons, tabs, page titles, form fields
• Modules – cards, forms, heroes, charts, tables, carousels
Elements
Elements are the smallest pieces of a design system, but they play a critical role in maintaining consistency and facilitating customization.
Designers must allow easy color and typeface customization while enforcing strict rules for icons, grids, borders, and spacing to achieve design consistency.
Components
Components are the parts of the design system users will interact with the most. So, here designers must focus on the user more than the brands. Flexibility is still important at the component level, but the changes are more subtle. Brands might change borders, corner shapes, or swap content from left to right and vice versa to customize components.

Customizing a White Label Design System Workflow
If designed correctly, it should be quick to change a white label design system to meet a brand’s requirements.
1. Designers start at the element level—changing colors and typography and uploading brand assets.
2. Next, designers modify components—adjusting component shapes (circle/rounded/square) and content configuration (for example, adding or removing an icon from a CTA button).
3. Designers use modules to build page layouts according to the customer’s requirements.
Instead of starting from scratch for every client, designers can use building blocks from a flexible design system to quickly design a white label product.
Agencies might build several white label design systems to accommodate various industries like restaurants, fitness, finance, and tech.